Aditya L1 - India's First Solar Mission
Introduction
The Indian Space
Research Organisation (Isro) is preparing for its next ambitious project that
could contribute significantly to our understanding of our solar system in the
aftermath of successful trips to Mars and the Moon. The planned Aditya-L1 solar
mission is set to shed light on the intricate operations of our Sun, the exact
thing that keeps life on Earth alive.
Our nearest star,
the Sun, makes it possible to examine stars in great detail, which is
challenging with other far-off stars. The dynamic activity on this celestial
planet extends far beyond its apparent surface. It occasionally unleashes
enormous energy bursts and displays a variety of eruptive characteristics.
However, these
solar flares might have an effect on our highly advanced society by disrupting
the near-Earth space environment. Early detection and action are crucial to
preventing any such disruptions. As a natural laboratory, the Sun offers an
invaluable setting for the study of these elusive phenomena, which cannot be
directly reproduced in any controlled laboratory setting.
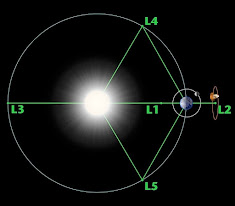
What is Lagrange point 1?
According to NASA,
a Lagrange point is a location in space where "the gravitational
attraction of two massive objects precisely equals the centripetal force
necessary for a small object to travel with them. By using these locations in
space, spacecraft can spend less fuel to maintain their position. This
basically means that at that time, an object put between two heavenly bodies
will effectively maintain its relative location while travelling with them due
to the gravitational attraction and repulsion between them.
Objectives of Aditya L1 Mission
The goals of the
Aditya-L1 mission are varied and include studying different aspects of solar
dynamics. These consist of studying
- Coronal heating
- The processes accelerating solar wind
- The beginning of flares and coronal mass ejections
- The complex dynamics of the solar atmosphere, as well as
- How solar wind and temperature anisotropy are distributed.
Payloads of Aditya L1
Each of the seven
tools the satellite is equipped with is designed to investigate a distinct
layer of the Sun. Three of these
payloads will perform on-the-spot particle and field analyses, while the other
four will be positioned at L1 to study the Sun directly.
- Visible Emission Line Coronagraph
- Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope
- Solar Low Energy X-Ray Spectrometer
- High Energy L1 Orbiting X-Ray Spectrometer
- Aditya Solar Wind Particle Experimentation
- Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya
- Advanced Tri-Axial High Resolution Digital Magnetometer
The Corona,
imaging, spectroscopy, and Coronal mass ejections will all be studied via the
Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC).
The narrow and
broad photosphere and chromosphere imaging will be the primary focus of the
Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT). Additionally, it will track changes
in solar irradiation.
The Soft and Hard
X-ray Flares from the Sun will be studied over a wide X-ray energy range by the
Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS) and High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray
Spectrometer (HEL1OS).
The electrons and
protons in the solar wind or particles will be analysed by the Aditya Solar
wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX) and the Plasma Analyzer Package for Aditya
(PAPA). It will also research the powerful ions.
The Advanced
Tri-axial High Resolution Digital Magnetometers will study the interplanetary
magnetic field at L1 point.
Conclusion
Aditya-L1 is a
fully indigenous effort with the participation of national institutions, an
ISRO official said. The nation's mission, which could fundamentally alter our
understanding of the mechanics of the Sun and space weather, is marked by this
significant project.
References
- https://www.isro.gov.in/Aditya_L1.html
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/aditya-l1-news-live-updates-isro-solar-mission-launch-sriharikota/liveblog/103231870.cms
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aditya-L1
- https://www-moneycontrol-com.cdn.ampproject.org/v/s/www.moneycontrol.com/news/india/aditya-l1-solar-mission-live-updates-isro-sriharikota-launch-11286671.html/amp?amp_gsa=1&_js_v=a9&usqp=mq331AQIUAKwASCAAgM%3D#amp_tf=From%20%251%24s&aoh=16934996774239&referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.com&share=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.moneycontrol.com%2Fnews%2Findia%2Faditya-l1-solar-mission-live-updates-isro-sriharikota-launch-11286671.html




Comments
Post a Comment